Spis treści
Proxmox
Przykładowy log z instalacji: Log
Wstęp
Instalujemy minimalną wersję Debiana - czyli: podstawowe narzędzia oraz SSH.
Użytkownik
Usuwamy użytkownika, którego założyliśmy podczas instalacji:
userdel -r -f devel
Instalacja
Podstawowe narzędzia
aptitude install bzip2 unzip p7zip-full mc subversion subversion-tools iptables-persistent telnet tcpdump unzip openvpn zip hdparm smartmontools git rsync
Repozytoria
echo "deb http://download.proxmox.com/debian wheezy pve" >> /etc/apt/sources.list wget -O- "http://download.proxmox.com/debian/key.asc" | apt-key add -
Uaktualnienie systemu
aptitude update && aptitude full-upgrade
Instalacja kernela
aptitude install pve-firmware pve-kernel-2.6.32-26-pve
Usuwamy stary kernel i aktualizujemy konfigurację Gruba:
apt-get remove linux-image-amd64 linux-image-3.2.0-4-amd64 linux-base
Po tej zmianie należy uruchomić ponownie serwer i sprawdzić czy jest uruchomiony na kernelu Proxmoxa:
root@proxmox:~# uname -r 2.6.32-26-pve
Instalacja Proxmoxa
aptitude install pve-headers-2.6.32-26-pve proxmox-ve-2.6.32 ntp lvm2 postfix ksm-control-daemon vzprocps open-iscsi bootlogd
Konfiguracja
Forwarding
Włączamy forwarding pakietów:
echo "ip_nat_ftp" >> /etc/modules echo "ip_conntrack_ftp" >> /etc/modules cat /etc/sysctl.conf | sed "s/\#net.ipv4.ip_forward\=1/net.ipv4.ip_forward\=1/g" > /etc/sysctl.conf.bak mv /etc/sysctl.conf.bak /etc/sysctl.conf sysctl -p
Konfigurujemy dodatkowe adresy IP - plik: /etc/network/interfaces.
SMART
Włączamy monitoring dysków:
cat /etc/default/smartmontools | sed "s/\#enable_smart\=\"\/dev\/hda\ \/dev\/hdb\"/enable_smart\=\"\/dev\/sda\ \/dev\/sdb\"/g" > /etc/default/smartmontools.bak cat /etc/default/smartmontools.bak | sed "s/\#start_smartd=yes/start_smartd\=yes/g" > /etc/default/smartmontools cat /etc/default/smartmontools | sed "s/\#smartd_opts\=\"--interval\=1800\"/smartd_opts\=\"--interval\=1800\"/g" > /etc/default/smartmontools.bak mv /etc/default/smartmontools.bak /etc/default/smartmontools cat /etc/smartd.conf | sed "s/DEVICESCAN\ -d\ removable\ -n\ standby\ -m\ root\ -M\ exec\ \/usr\/share\/smartmontools\/smartd-runner/DEVICESCAN\ -d\ removable\ -n\ standby\ -m\ admin@domain.ltd\ -M\ exec\ \/usr\/share\/smartmontools\/smartd-runner/g" > /etc/smartd.conf.bak mv /etc/smartd.conf.bak /etc/smartd.conf
MDADM
Włączamy monitoring macierzy RAID:
cat /etc/mdadm/mdadm.conf | sed "s/MAILADDR\ root/MAILADDR\ admin@domain.ltd/g" > /etc/mdadm/mdadm.conf.bak mv /etc/mdadm/mdadm.conf.bak /etc/mdadm/mdadm.conf
Reboot
Uruchamiamy ponownie serwer i sprawdzamy czy SMART i MDADM wstały, czy forwarding jest włączony i sieć poprawnie skonfigurowana.
/etc/init.d/smartmontools status /etc/init.d/mdadm status cat /proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_forward ip add
Bezpieczeństwo
Zmieniamy domyślny port SSH:
nano /etc/ssh/sshd_config /etc/init.d/ssh restart
Zmieniamy hasło na root'a jeśli mamy proste na bardziej skomplikowane:
passwd
Dopisujemy swoje klucze do pliku /root/.ssh/authorized_keys.
Firewall
Tu w zależności od sieci. Przykładowy plik:
#!/bin/bash ### VARS ethNet="eth0" ethLan="vmbr0" ethVpn="tap0" netLan="10.1.2.0/24" netVpn="10.1.3.0/24" IPHE1="10.2.2.168" IPHE2="10.2.2.106" IPALLOW="192.1.1.0/24" serverVirt="10.1.2.101" if [ "$1" = "start" ]; then echo "Starting router firewall..." ### POLICY POLICY="DROP" iptables -P OUTPUT ACCEPT iptables -P INPUT $POLICY iptables -P FORWARD $POLICY ### DROP # Block spoof address localhost other interfaces with the exception lo iptables -A INPUT -t filter ! -i lo -s 127.0.0.0/8 -j DROP # Block spoof address private networks in wan interface iptables -A INPUT -i $ethNet -s 10.0.0.0/8 -j DROP iptables -A INPUT -i $ethNet -s 172.16.0.0/12 -j DROP iptables -A INPUT -i $ethNet -s 192.168.0.0/16 -j DROP # Flood protection iptables -A INPUT -m limit --limit 1/hour -j LOG iptables -A INPUT -i $ethNet -p icmp --icmp-type echo-request -m limit --limit 1/s -j ACCEPT # ping of death #Block invalid packet iptables -A INPUT -i $ethNet -p tcp -m state --state INVALID -j DROP ### ACCEPT # Accept all packets in localhost iptables -A INPUT -t filter -i lo -j ACCEPT iptables -A OUTPUT -t filter -o lo -j ACCEPT iptables -A FORWARD -t filter -o lo -j ACCEPT # Accept established and related connection iptables -A INPUT -i $ethNet -m state --state ESTABLISHED,RELATED -j ACCEPT iptables -A INPUT -i $ethLan -m state --state ESTABLISHED,RELATED -j ACCEPT iptables -A INPUT -i $ethVpn -m state --state ESTABLISHED,RELATED -j ACCEPT # Accept ping iptables -A INPUT -p icmp -j ACCEPT iptables -A FORWARD -p icmp -j ACCEPT # Accept output connection iptables -A OUTPUT -o $ethNet -j ACCEPT iptables -A OUTPUT -o $ethLan -j ACCEPT iptables -A INPUT -i $ethLan -j ACCEPT # VPN iptables -A OUTPUT -o $ethVpn -j ACCEPT iptables -A INPUT -i $ethVpn -j ACCEPT # IP ALLOW for ipa in $IPALLOW do iptables -A INPUT -s $ipa -j ACCEPT done ## Services # SSH iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 12345 -j ACCEPT # HTTP iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 80 -j ACCEPT # HTTPS iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 443 -j ACCEPT # VPN #iptables -A INPUT -p udp --dport 1144 -j ACCEPT #iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 1144 -j ACCEPT ## FORWARD # Forward new connection to Lan network iptables -A FORWARD -d $netLan -p tcp -m state --state NEW -j ACCEPT # Forward established and related connection iptables -A FORWARD -t filter -p tcp -m state --state ESTABLISHED,RELATED -j ACCEPT iptables -A FORWARD -t filter -p udp -m state --state ESTABLISHED,RELATED -j ACCEPT iptables -A FORWARD -t filter -p icmp -m state --state ESTABLISHED,RELATED -j ACCEPT # Forward from Lan network iptables -A FORWARD -s $netLan -j ACCEPT iptables -A FORWARD -s $netVpn -j ACCEPT iptables -A FORWARD -s 192.1.1.0/24 -j ACCEPT ### DNAT (services in Lan) # server virt iptables -t nat -A PREROUTING --dst $IPHE2 -p tcp --dport 443 -j DNAT --to-destination $serverVirt:8443 ### SNAT (maskarada) # Set address for server Srutex iptables -t nat -A POSTROUTING -o $ethNet -s $serverVirt -j SNAT --to $IPHE2 # Set address for Lan iptables -t nat -A POSTROUTING -o $ethNet -s $netLan -j SNAT --to $IPHE1 # Other in LAN iptables-save > /etc/iptables/rules.v4 fi if [ "$1" = "stop" ]; then echo "Stopping router firewall..." iptables -F INPUT iptables -F OUTPUT iptables -F FORWARD iptables -t nat -F iptables -t nat -F POSTROUTING iptables -t nat -F PREROUTING iptables -t mangle -F iptables -t mangle -F POSTROUTING iptables -t mangle -F PREROUTING # Flush firewall rules (-F before -X) iptables -t filter -F iptables -t nat -F iptables -t mangle -F # Delete firewall chains iptables -t filter -X iptables -t nat -X iptables -t mangle -X # Set counter to zero iptables -t filter -Z iptables -t nat -Z iptables -t mangle -Z # Default policy iptables -P INPUT ACCEPT iptables -P OUTPUT ACCEPT iptables -P FORWARD ACCEPT fi if [ "$1" = "restart" ]; then $0 stop $0 start fi if [ "$1" = "" ]; then echo "Usage: $0 [start|stop|restart]" fi
zapisujemy do /root/firewall.sh i nadajemy odpowiednie uprawnienia:
chmod 700 /root/firewall.sh
Wykonujemy:
/root/firewall.sh restart
Wykonujemy restart serwera i sprawdzamy czy firewall jest ustawiony:
iptables -n -L
Sieć wirtualna
Należy stworzyć podsieć na potrzeby komunikacji z serwerami wirtualnymi, ja wykorzystuję podsieć z puli prywatnych - tą, która podałem w firewallu. Klikamy wg poniższego zrzutu ekranu:
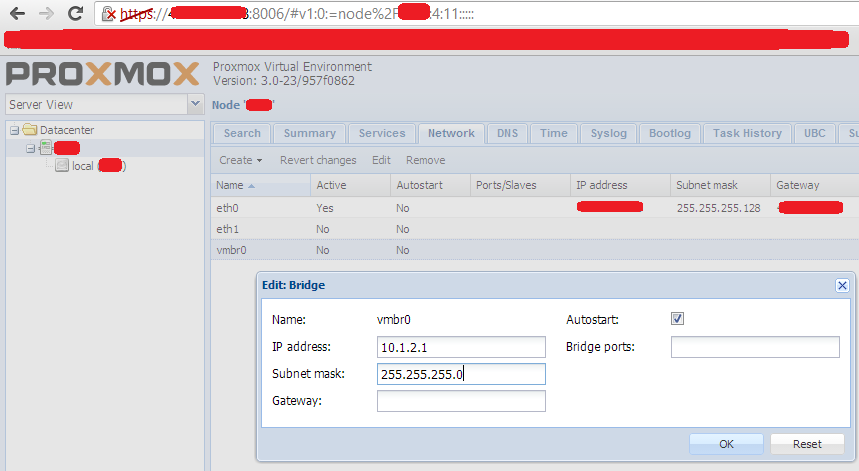
Po kliknięciu OK należy wykonać restart serwera, ale uwaga! W moim przypadku Proxmox usunął z konfiguracji sieci wpis:
allow-hotplug eth0
Należy edytować plik /etc/network/interfaces.new i dopisać w/w wpis bezpośrednio przed:
iface eth0 inet static
Po upewnieniu się, że konfiguracja jest poprawna należy wykonać restart serwera.
Komunikat o subskrypcji
Jeśli irytuje nas komunikat o nie wykupionej subskrypcji to możemy go wyłączyć modyfikując kod:
cp /usr/share/pve-manager/ext4/pvemanagerlib.js /usr/share/pve-manager/ext4/pvemanagerlib.js.bak
export test0="data.status !== 'Active'"
cat /usr/share/pve-manager/ext4/pvemanagerlib.js | sed "s/${test0}/false/g" > /usr/share/pve-manager/ext4/pvemanagerlib.js.new
mv /usr/share/pve-manager/ext4/pvemanagerlib.js.new /usr/share/pve-manager/ext4/pvemanagerlib.js
Wirtualki
Dodawanie
Klikamy:
- Create VM,
- podajemy nazwę wirtualnej maszyny - nazwa musi być zgodna z domeną - czyli najlepiej same litery, znaki i ew „-”,
- zaznaczamy odpowiedni system operacyjny, w przypadku Debiana będzie to Linux 3.x/2.6.x Kernel,
- aby zainstalować system należy podmontować obraz iso do wirtualnej maszyny, w tym celu należy wybrać obraz iso, lista wyboru obrazów jest zależna od tego co się znajduje w katalogu /var/lib/vz/template/iso na maszynie fizycznej,
- dysk twardy, ja zalecam wybieranie Bus/Device: Virtio i Format: RAW,
- CPU: jeśli jest to Linuks to zazwyczaj wybieram maszyny 64bitowe - czyli domyślnie kvm64, w przypadku Windowsów w zależności od posiadanej wersji: kvm32 lub kvm64,
- Network: jeśli na wirtualnej maszynie będzie Linuks to wybieramy e1000 lub VirtIO, w przypadku Windowsów E1000.
- klikamy na Finish.
Po stworzeniu wirtualnej maszyny klikamy na nią oraz wybieramy Console - maszyna nie jest jeszcze włączona. Po otworzeniu się nowego okienka w przeglądarce uruchomi się konsola, która wymaga Javy! Aplet Javy połączy się za pomocą przeglądarki (z naszego komputera) do maszyny fizycznej - i tu mała uwaga będzie się łączył na porty 5900-n - gdzie n to ilość otartych konsol na serwerze - te porty należy odblokować dla naszych IP, z których będziemy się łączyć. Po uruchomieniu się konsoli oraz apletu Javy należy kliknąć na Start.
Forwardowanie ruchu
Forwardować ruch możemy na dwa sposoby, za pomocą firewall'a - sekcja DNAT lub za pomocą Nginx'a w trybie revProxy - w przypadku ruchu HTTP.
Regułka dla firewalla:
iptables -t nat -A PREROUTING --dst $IPZEW -p tcp --dport $PORT_NA_IP_ZEW -j DNAT --to-destination $IPWEW_WIRTUALKI:$PORT_WIRTUALKI
Nginx - przykładowy Vhost:
server {
listen 443;
server_name vhostname.domain.ltd;
ssl on;
ssl_certificate cert.crt;
ssl_certificate_key cert.key;
ssl_session_timeout 5m;
ssl_protocols SSLv3 TLSv1;
ssl_ciphers ALL:!ADH:!EXPORT56:RC4+RSA:+HIGH:+MEDIUM:+LOW:+SSLv3:+EXP;
ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
location / {
proxy_pass http://10.1.2.101:80;
proxy_next_upstream error timeout invalid_header http_500 http_502 http_503 http_504;
proxy_redirect off;
proxy_buffering off;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
}
}
W przypadku Nginx'a należy najpierw zainstalować oraz odblokować porty, na których będzie nasłuchiwał:
aptitude install nginx
Przenoszenie na innego Proxmoxa
Przy przenoszeniu należy wyłączyć maszynę wirtualną, zarchiwizować plik RAW, który znajduje się w /var/lib/vz/images/101/vm-101-disk-1.raw ← gdzie 101 to ID maszyny z panelu Proxmoxa, archiwizacja:
tar czf /var/lib/vz/images/101/vm-101-disk-1.raw.tgz /var/lib/vz/images/101/vm-101-disk-1.raw
Po spakowaniu należy skopiować plik tgz na nowy serwer. Na nowym serwerze należy stworzyć wirtualną maszynę z uwzględnieniem ustawień maszyny na starym Proxmoksie, czyli:
- typ systemu operacyjnego,
- typ kontrolera,
- format dysku wirtualnego,
- typ karty sieciowej oraz mac address.
Należy wypakować plik tgz i podmienić go z nowo stworzonym plikiem nowej wirtualki.